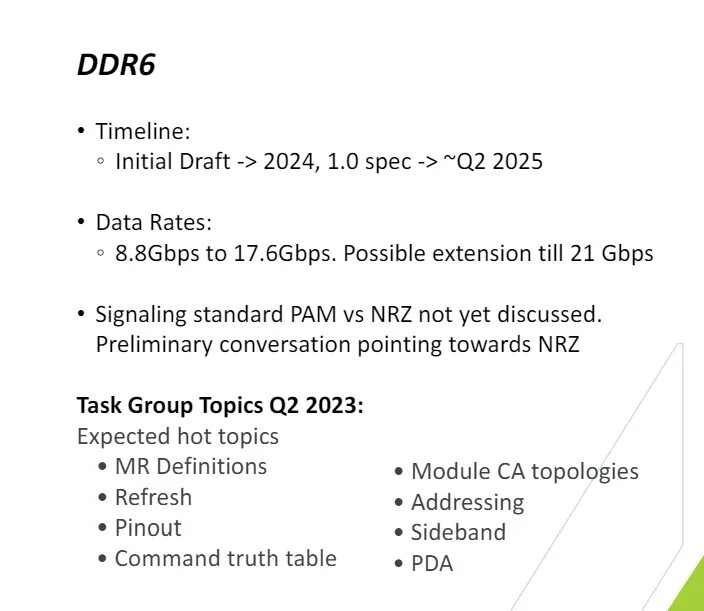
The upcoming PC DDR6 memory standard (not to be confused with GDDR6) is set to provide a significant boost in bandwidth compared to DDR4. According to a presentation by Synopsys, a leading provider of memory controller and PHY IP blocks, DDR6 will offer a 10-fold increase in bandwidth. The initial version of the DDR6 specification by JEDEC is projected to be finalized by 2024, with version 1.0 expected to be ready by mid-2025. The data rates for DDR6 will start at DDR6-8800 and go up to DDR6-17600 in the first generation, with future iterations potentially reaching DDR6-21333 (or 21 Gbps). This represents a tenfold increase in bandwidth compared to DDR4-2133, the original speed of DDR4 introduced almost a decade ago with 6th Gen Core "Skylake" processors. It is logical for a memory standard developed a decade later to offer such a significant increase in bandwidth.
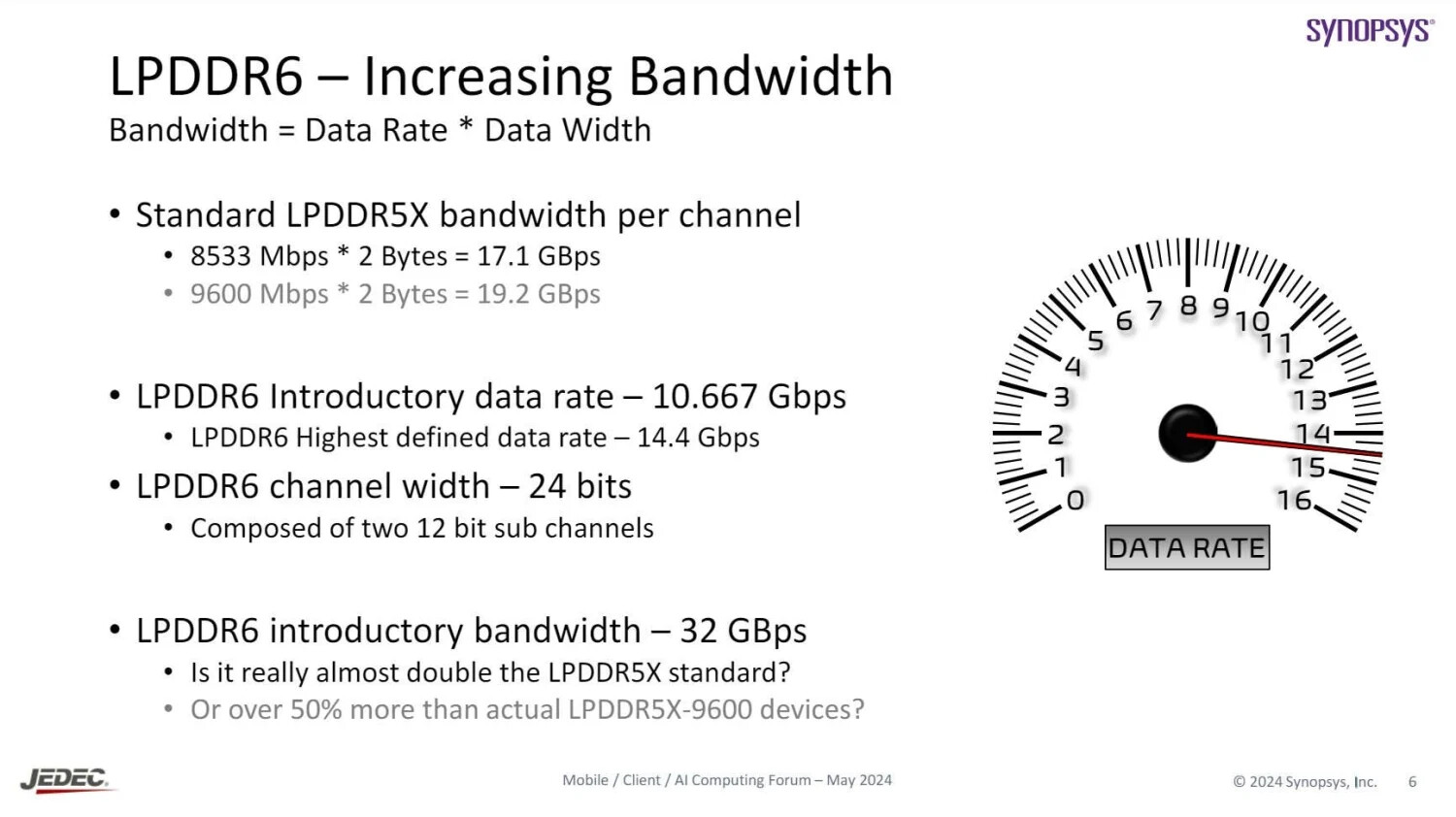
In addition to discussing DDR6, Synopsys also mentions LPDDR6 in their presentation. LPDDR6 is the future low-power memory standard designed for thin-and-light laptops and smartphones. The initial data rate for LPDDR6 will be LPDDR6-10667 across a 24-bit memory channel with two 12-bit sub-channels. The highest defined data rate for LPDDR6 is anticipated to be LPDDR6-14400 (likely 14466 MT/s). Along with the increase in bandwidth across generations, both PC DDR6 and LPDDR6 are expected to introduce various security and energy-efficient features. This includes an "efficiency mode" that reduces idle power consumption for the memory devices.